Electric garment steamer is a household or commercial device used to remove wrinkles and refresh clothing and fabrics using heated steam. Unlike traditional irons, which press fabric against a flat surface, a garment steamer produces a continuous stream of steam that relaxes fibers and smooths wrinkles without direct contact.
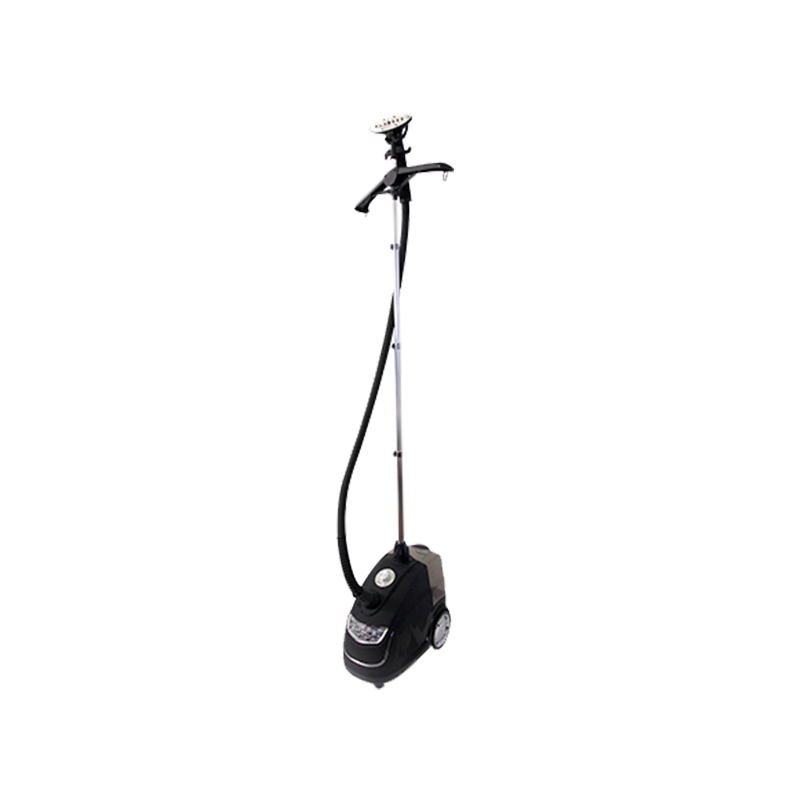

Components: Electric garment steamers typically consist of a water reservoir, heating element, steam nozzle, power switch, and a hose or telescopic pole in vertical models.
Operation: Water in the reservoir is heated to generate steam, which is then directed onto garments through the nozzle.
Types: Standalone vertical steamers, handheld steamers, and travel-sized steamers are common, offering different levels of portability and capacity.
Applications: Used for clothing maintenance, curtain refreshing, upholstery care, and some light fabric cleaning tasks.
Safety Features: Many models include automatic shut-off mechanisms, temperature regulation, and anti-drip designs to prevent accidental burns or water leakage.
Electric garment steamers provide a convenient way to smooth fabric without the pressing effect of an iron, reducing the risk of shine or damage on delicate materials. The design supports both domestic and commercial applications, with variations in size, heating capacity, and water tank volume.
Why Do Electric Garment Steamers Exist?
Ease of Use
Electric garment steamers exist to simplify the process of removing wrinkles and refreshing garments. Unlike traditional irons, steamers do not require a flat surface, allowing garments to remain hanging while being treated. This convenience saves time and reduces effort, particularly for delicate or structured clothing that may be difficult to press.
Fabric Safety
Some fabrics, such as silk, polyester, or wool blends, are sensitive to high direct heat. Steamers provide a gentler alternative to irons, relaxing fibers with steam rather than pressing them. This reduces the risk of burns, shine marks, or distortion of the garment.
Versatility in Applications
Beyond clothing, electric garment steamers can be used for curtains, upholstery, linens, and soft toys. The steam penetrates fibers, helping remove wrinkles and odors without requiring removal or disassembly. This versatility makes steamers a practical tool for both household and commercial textile maintenance.
Efficiency and Time Saving
Steamers heat quickly and produce continuous steam, allowing multiple garments or items to be treated in a short period. They are particularly useful in busy environments, such as hotels, dry cleaners, or fashion stores, where speed and ease of operation are important.
Electric Garment Steamer Manufacturing Process Issues
Component Assembly Challenges
Manufacturing an electric garment steamer involves assembling several precise components, including the heating element, water reservoir, steam nozzle, and control switches. Ensuring proper alignment and sealing of these components is essential to prevent leaks or electrical faults. Misalignment can result in reduced steam flow, water leakage, or uneven heating.
Material Selection and Durability
Selecting appropriate materials for the water reservoir, nozzle, and casing is crucial. Plastics must withstand repeated heating without deformation, while metals need corrosion resistance to avoid rusting from prolonged exposure to water and steam. Inadequate material choices can bring about early failure or safety hazards.
Quality Control of Electrical Components
The heating element and control circuitry must meet safety standards for electrical appliances. Faulty wiring, insufficient insulation, or inconsistent heating can pose burn or fire risks. Proper testing and quality assurance are essential to ensure operational reliability and user safety.
Steam Flow and Pressure Issues
During production, the internal channels for steam must be designed for consistent flow. Narrow or misaligned channels may cause clogging, uneven steam output, or overheating of the heating element. Calibration of pressure and flow is necessary to achieve efficient steaming performance.
Safety and Certification Compliance
Electric garment steamers must comply with national and international safety standards. During manufacturing, testing for overheat protection, automatic shut-off, and leakage prevention is critical. Failure to meet safety regulations can prevent the product from reaching the market.


 Language
Language  English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español русский
русский








